 |
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Goddard Space Flight Center |
SEARCH NASA |
 MOLA MOLA |
Results from MGS Aerobraking Hiatus Orbits
Profiles Presented at the Fall Meeting of the American Geophysical Union
San Francisco, December 9, 1997
Background
During a hiatus in the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft aerobraking sequence, the science instruments were able to collect data. The MOLA instrument obtained over 200,000 observations at altitudes less than 470 miles (786 km), which resulted in profiles of topography in the north-south direction as the instrument ranged for approximately 22 minutes during each orbit. Eighteen profiles were collected before aerobraking resumed. The locations of the profiles and the profiles themselves are shown below. Note that these data are still being corrected. Final versions will be submitted to the NASA Planetary Data System (PDS) for archiving in early February, 1998.
Summary of data collected in Calibration Pass and in the Aerobraking Hiatus Orbit: Periapse Number, Date, Time, Equator-crossing Longitude (areocentric, positive E):
- 03, September 15, 3:30 PM EDT, 336°E (Western Elysium)
- 20, October 14, 5:00 PM EDT, 133.1°E
- 21, October 15, 8:30 PM EDT, 335.4°E (Western Elysium, Mie crater)
- 22, October 17, 8:00 AM EDT, 177.7°E (Amazonis Planitia)
- 23, October 18, 7:30 PM EDT, 20°E
- 24, October 20, 7:00 AM EDT, 222°E (Olympus Mons)
- 25, October 21, 6:30 PM EDT, 64°E (Chryse)
- 26, October 23, 6:00 AM EDT, 266°E (Uranius Tholus, Syria Planum)
- 27, October 24, 5:23 PM EDT, 108°E
- 28, October 26, 3:47 AM EDT, 310°E (Chryse; most data lost due to Denver snowstorm)
- 29, October 27, 3:10 PM EDT, 153°E (Eastern Elysium)
- 30, October 29, 2:30 AM EDT, 356°E
- 31, October 30, 1:54 PM EDT, 199°E (Arcadia Planitia, Amazonis Planitia)
- 32, November 1, 1:18 AM EDT, 41°E
- 33, November 2, 12:45 PM EDT, 244°E (Tharsis; Arsia Mons)
- 34, November 4, 12:10 AM EDT, 86°E (Utopia Planitia, Isidis)
- 35, November 5, 11:31 AM EDT, 288°E (Valles Marineris)
- 36, November 6, 10:53 PM EDT, 131°E
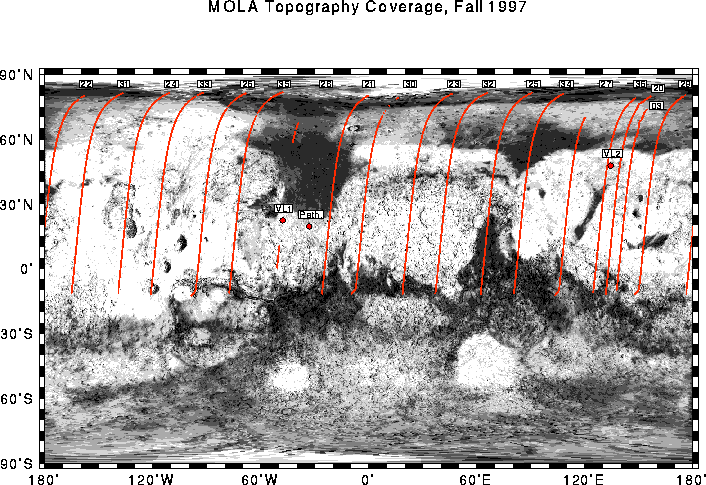
Locations of MOLA tracks during the capture orbit (Pass 03) and aerobraking hiatus period (Passes 20-36). Track numbers correspond to the number of spacecraft periapse, the point of spacecraft closest approach to Mars in a given orbit. Note that the MOLA command upload did not occur in Pass 28 and almost no data was obtained along that track. Also note the east positive longitude convention denoting profile locations. (Credit: MOLA Science Team)
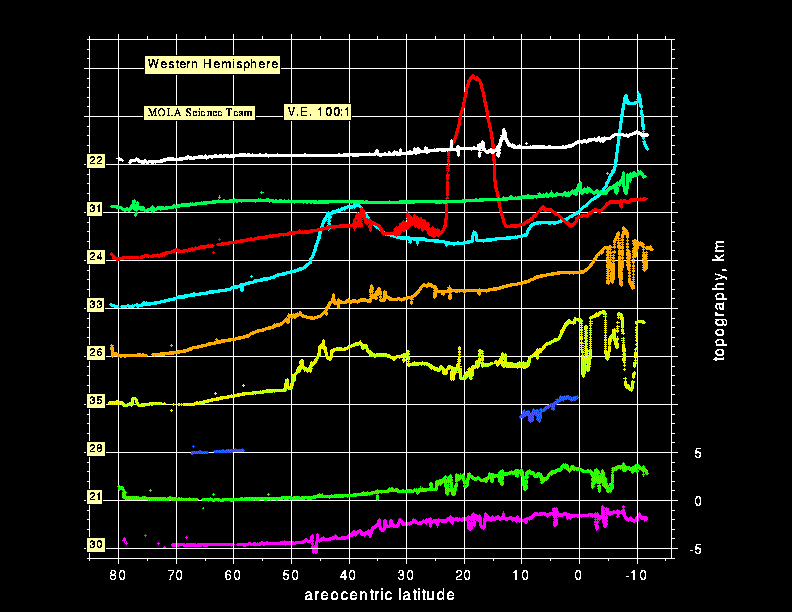
Topographic profiles of the western hemisphere of Mars obtained by the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) while the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft was in a 35-hour orbit around Mars. The vertical exaggeration in the plot is 100:1. (Credit: MOLA Science Team)
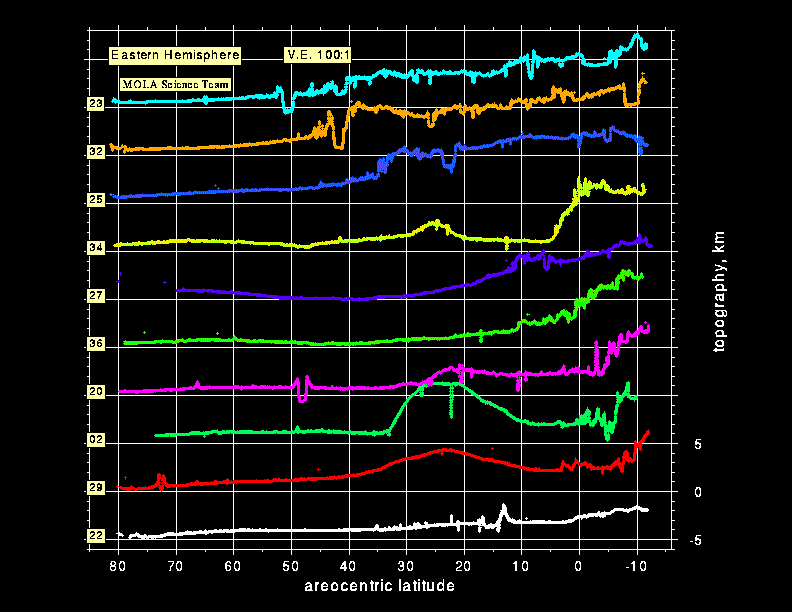
Topographic profiles of the eastern hemisphere of Mars obtained by the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) while the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft was in a 35-hour orbit around Mars. The vertical exaggeration in the plot is 100:1. (Credit: MOLA Science Team)
Return to the MOLA Science homepage
